Kubernetes Port Forward 机制
2016, Nov 22
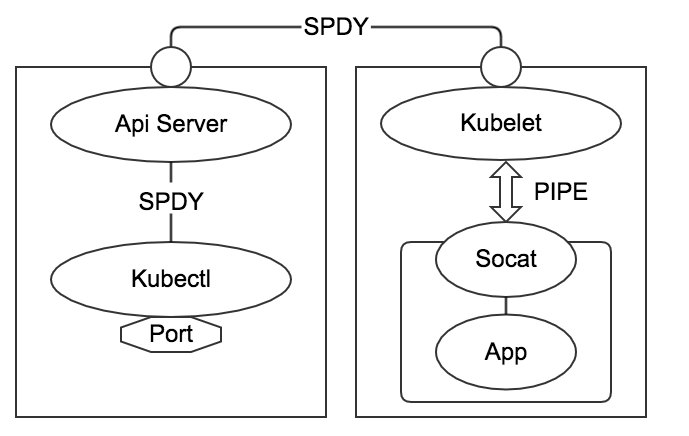
使用 kubectl 创建 port-forward 后,kubectl 会主动监听指定的本地端口。
kubectl port-forward pod-name local-port:container-port
当向 local-port 建立端口连接,并向该端口发送数据,数据经过以下步骤:
- 数据发往 kubctl 监听的 local-port
- kubectl 使用事先建立的与 ApiServer:8080 的链接,通过 SPDY 协议将数据发送给 ApiServer
- ApiServer 使用事先建立的与目标 pod 所在的 node 的 Kubelet 链接,通过 SPDY 协议将数据发送到目标 node
- 目标 node 的 Kubelet 收到数据后,通过 PIPE(STDIN,STDOUT)与 Socat 通信
- Socat 将 STDIN 的数据发送给 pod 内部的指定的 container-port,并将返回的数据写入到 STDOUT
- STDOUT 的数据由 Kubelet 接收并按照相反的路径发送回去
- 注:SPDY 协议将来可能会被替换为 HTTP/2*
nsenter 与 socat
nsenter 可以将指定的程序放置到另一个进程的 Namespace 中运行
-t, --target <pid> target process to get namespaces from
-m, --mount[=<file>] enter mount namespace
-u, --uts[=<file>] enter UTS namespace (hostname etc)
-i, --ipc[=<file>] enter System V IPC namespace
-n, --net[=<file>] enter network namespace
-p, --pid[=<file>] enter pid namespace
-C, --cgroup[=<file>] enter cgroup namespace
-U, --user[=<file>] enter user namespace
-S, --setuid <uid> set uid in entered namespace
-G, --setgid <gid> set gid in entered namespace
--preserve-credentials do not touch uids or gids
-r, --root[=<dir>] set the root directory
-w, --wd[=<dir>] set the working directory
-F, --no-fork do not fork before exec'ing <program>
例如,将 netstat 放置到与指定 PID 的进程相同的 net namespace 中运行:
nsenter -t $PID -n netstat
即可输出 PID 所在的 net namespace 的链接情况。
socat 可以实现流的代理与转发:
-,STDIN,STDOUT :表示标准输入输出,可以就用一个横杠代替
/var/log/syslog : 打开一个文件作为数据流。
TCP:: : 建立一个 TCP 连接作为数据流,TCP 也可以替换为 UDP
TCP-LISTEN: : 建立 TCP 监听端口,TCP 也可以替换为 UDP
EXEC: : 执行一个程序作为数据流。
例如:
socat - TCP4:localhost:80
即可实现写入 STDIN 的数据发往 localhost:80,localhost:80 的数据输出到 STDOUT。
Kubelet 与容器的通信
Kubelet 同时使用了 nsenter 和 socat 的功能:
nsenter -t $PID -n socat - TCP4:localhost:80
其中 $PID 为容器在 host 上的进程 ID。并且 socat 与 $PID 在同一个 net namespace 中,因此 localhost 即是容器内部的地址。
发送到 STDIN 的数据会经由 socat 发送到容器内部的 80 端口中,而 80 端口返回的数据则由 socat 输出到 STDOUT 中。
Kubelet 在调用该命令时,获取了命令的 STDIN 和 STDOUT 流,将数据写入 STDIN,并从 STDOUT 读取返回的数据,以此实现 Kubelet 与容器的通信。